The recent UK bonds selloff has captured significant attention in financial circles, marking a pivotal moment for the bond market. This sharp decline has notable implications, particularly on rising borrowing costs that affect consumers and businesses alike. Understanding the dynamics of the UK bonds selloff is essential as we navigate these changes.
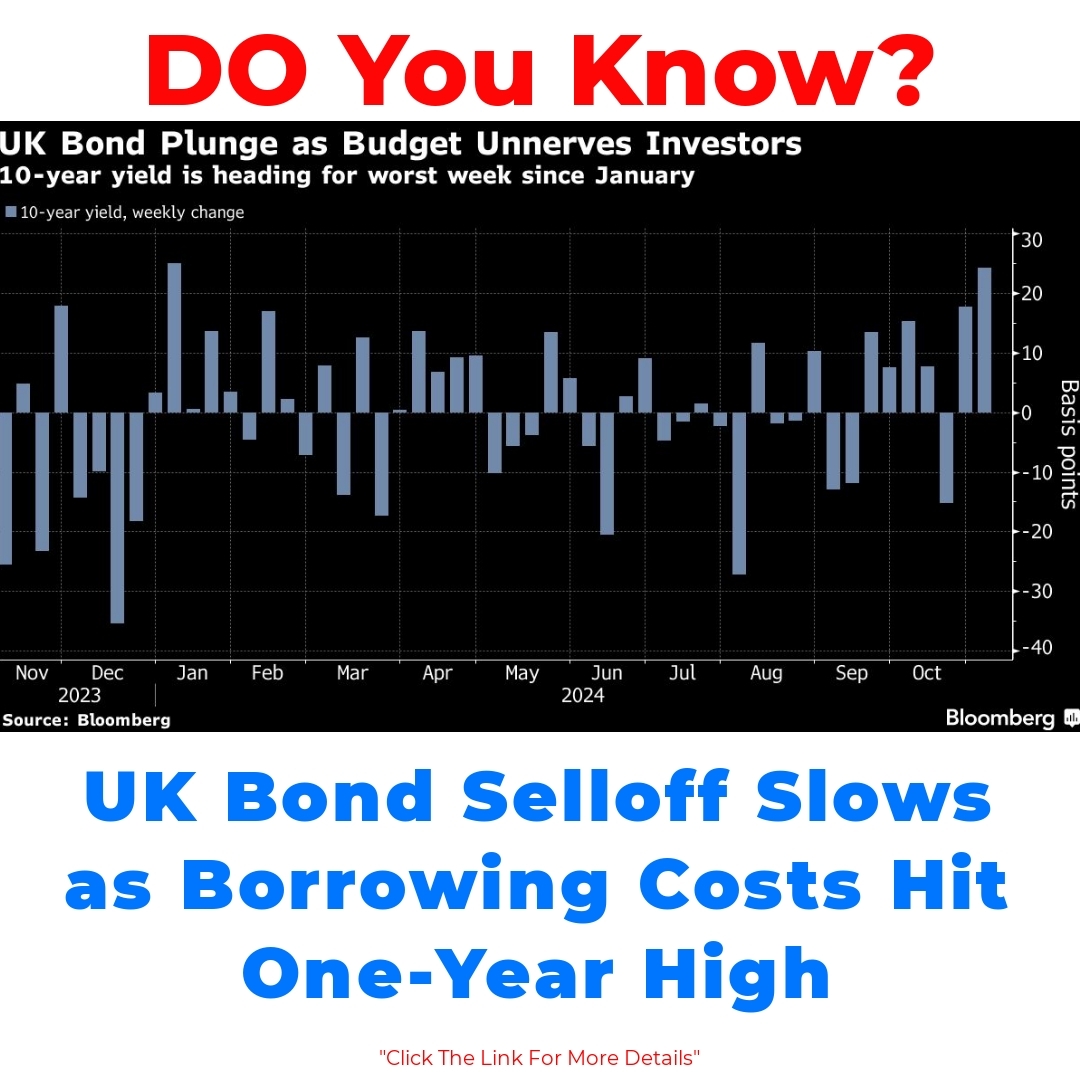
What Triggered the Sharp Selloff in UK Bonds?
The sharp selloff in UK bonds was triggered by several interconnected factors that rattled the market. We saw a significant shift in investor sentiment as uncertainties surrounding interest rates began to swell. With inflation not easing as expected, investors started to expect higher interest rates for a longer period. This change in perception about future economic conditions led to a hike in bond yields, compelling many to sell their holdings.
Market volatility played a substantial role in this selloff. Investors were faced with rapidly changing economic conditions, which created a domino effect across the bond market. The fear of rising borrowing costs started to dominate conversations, leading to increased selling pressure on UK government bonds. The combination of these factors painted a bleak picture and resulted in a swift decline in the bond market.
Implications of Rising Borrowing Costs in the UK
The implications of the UK bonds selloff extend far beyond the bond market itself. As borrowing costs rise, it becomes more expensive for consumers and businesses to secure loans. This environment could hinder investment activities and spending, both crucial for economic growth. For individuals looking to buy homes or cars, higher borrowing costs could result in inflated monthly payments, limiting their purchasing power.
Businesses aren’t spared either. Higher borrowing costs will likely lead to increased expenses, which could subsequently affect pricing strategies. Firms might pass on these costs to consumers, leading to a ripple effect throughout the economy. It’s essential to consider how these dynamics interplay, especially as we analyze the broader implications of rising borrowing costs in the UK.
Understanding the Bond Market and Investment Strategies
Grasping the dynamics of the bond market is crucial, particularly in light of the recent selloff in UK government bonds. This event has underscored the necessity for investors to reassess their strategies. With expectations of increased interest rates and fluctuating bond yields, now is the time to consider adaptive investment strategies. Diversifying portfolios to include different asset classes can help mitigate risks associated with rising borrowing costs.
Additionally, fixed-income investors might want to rethink their allocations. Investing in shorter-duration bonds can be a strategic move to shield against market volatility. As the bond market continues to undergo significant changes, having a flexible approach can provide a buffer against sudden shifts that influence overall investment returns.
Consequences for the Economy: A Broader Perspective
The sharp selloff in UK bonds carries substantial consequences for the economy at large. As borrowing costs rise, consumer spending may slow down, leading to a decline in economic activity. Market reactions tend to be sensitive to these developments; if businesses pull back on investments due to high financing costs, it would likely induce a slowdown in economic growth.
Furthermore, if the selloff leads to a sustained increase in bond yields, this could signal future interest rate hikes. Such predictions exacerbate market volatility, sparking uncertainty among investors and consumers alike. Understanding the economic impact of the recent selloff is not merely about current conditions; it also involves forecasting future trends and adjusting accordingly.
How UK Bond Market Affects Borrowing Costs
The relationship between the UK bond market and borrowing costs is quite significant. As bond yields rise, it directly influences the cost of borrowing across different sectors. For instance, lenders often base their interest rates on government bond yields; hence, as these yields rise, mortgage rates, personal loans, and business loans follow suit.
This correlation emphasizes the importance of keeping an eye on bond market trends. Understanding how the UK bond market affects borrowing costs can help consumers and businesses make informed decisions, such as locking in fixed-rate financing before rates increase further.
Understanding Market Reactions to Bond Selloffs
To gain insight into the current situation, we can look back at past selloffs and their outcomes. Typically, market reactions can be dramatic, with investors rushing to cash out as prices drop. Understanding market reactions to bond selloffs can aid in predicting future movements and adjusting strategies accordingly. Historical data shows that selloffs often precede larger economic shifts, underscoring the potential long-term effects of today’s actions.
In similar past events, markets have shown resilience over time, often bouncing back after an initial shock. However, the speed at which this recovery occurs can depend significantly on how high borrowing costs are and whether they stabilize or continue to rise. Investors would benefit from closely monitoring these patterns and being prepared to adjust their financial plans for the best outcomes.
Conclusion
In summary, the UK bonds selloff has critical implications not just within the bond market but also across the broader economy. As we witness rising borrowing costs affecting both consumers and businesses, the landscape is rapidly changing. Keeping these factors in mind will be essential for both short-term and long-term planning.
As we look toward the future, it’s crucial to remain vigilant about market trends and potential interest rate changes. The ongoing situation with the UK bonds selloff serves as a reminder of how interconnected our financial systems can be, influencing diverse aspects of our economy.
FAQ
What caused the recent selloff in UK bonds?
The recent selloff in UK bonds was primarily driven by shifting investor sentiments due to rising uncertainties around interest rates and inflation. As inflation persisted, investors anticipated that interest rates would remain higher for an extended period, leading to increased bond yields and selling pressure.
How do rising borrowing costs impact consumers?
As borrowing costs increase, loans become more expensive for consumers. This means higher monthly payments for mortgages and personal loans, potentially reducing purchasing power and limiting consumer spending.
What effects does the selloff have on businesses?
Businesses face higher borrowing costs, which can lead to increased expenses. This may affect their pricing strategies, pushing them to pass these costs onto consumers, further influencing economic activity.
How can investors adjust their strategies following the selloff?
Investors should consider diversifying their portfolios and may want to invest in shorter-duration bonds to guard against market volatility. Adapting their strategies now can help mitigate risks associated with rising borrowing costs.
What are the potential economic consequences of the bond selloff?
A selloff in bonds can slow consumer spending and economic activity. If businesses reduce their investments due to high financing costs, this can lead to a broader economic slowdown.
What is the link between the bond market and borrowing costs?
There’s a strong connection between the bond market and borrowing costs. As bond yields rise, lenders often increase their interest rates on loans, impacting mortgages, personal loans, and business loans.
How have markets historically reacted to bond selloffs?
Typically, investors react dramatically to bond selloffs, often cashing out rapidly. While markets have shown resilience and bounce-back capability after such events, the speed of recovery varies based on borrowing costs and stabilization.





