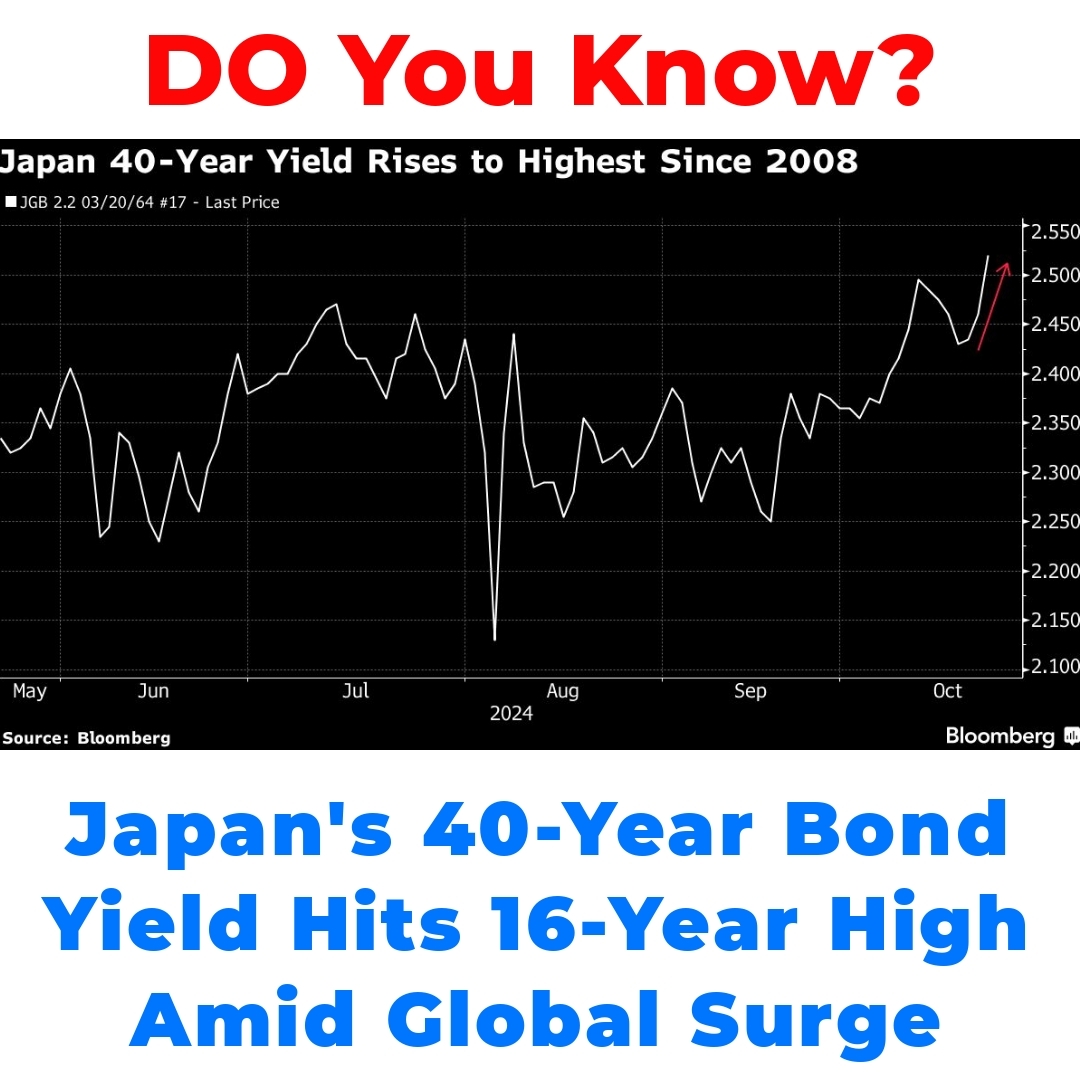
The Japan 40-year government bond yield has surged to its highest point in 16 years, prompting critical analysis of bond market dynamics. Understanding this rise is essential in the broader context of global yields and the potential impacts of US Federal Reserve rate cuts on the financial landscape.

Understanding the Japan 40-Year Government Bond Yield
The Japan 40-year government bond yield is a critical indicator in the financial markets. Essentially, it represents the interest rate the Japanese government pays to borrow money for four decades. As bonds are seen as low-risk investments, changes in their yields often signal broader economic trends. When yields rise, it usually indicates that investors expect higher inflation or interest rates in the future.
In the past 16 years, we’ve seen the Japan 40-year government bond yield fluctuate significantly. Following a long period of low yields, the current surge marks a notable departure from the trends we’ve observed in the past.
The Surge in Global Yields
The recent increase in the Japan 40-year government bond yield is heavily influenced by shifts in global yields. Various factors contribute to this rise—not just in Japan, but worldwide. Economic indicators, such as inflation rates and employment figures, play a huge role. For instance, when economies show signs of strong growth, central banks may respond by raising interest rates, pushing global yields upward.
Additionally, global market dynamics, including changes in interest rates in other major economies, like the U.S., have a ripple effect. The interconnectedness of the global financial system means that a rise in yields elsewhere can directly impact the Japanese bond market.
Traders Reassessing the US Federal Reserve Rate Cut Strategy
Traders are currently reassessing what the US Federal Reserve’s rate cuts mean for bond markets, particularly in Japan. When the Federal Reserve alters its monetary policy, it often sends waves through the global markets. Lower rates in the U.S. can lead to increased investments in foreign bonds, including Japanese ones, affecting the Japan 40-year government bond yield directly.
Understanding how these American policy decisions influence Japanese bonds is essential for investors. As the Federal Reserve navigates its strategies, bond investors will need to stay alert to how these changes can affect their portfolios.
Bond Market Trends and Their Implications
Currently, we are witnessing significant bond market trends that are shaping the Japan 40-year government bond yield. The relationship between bond yields and interest rates is crucial. As interest rates rise globally, yields on government bonds like Japan’s tend to climb as well. This change can range from a gradual increase to sudden surges, reflecting investor sentiment and market conditions.
For bond investors, navigating these trends involves understanding the broader context and timing their investments accordingly. Being aware of how economic shifts in one part of the world can affect bond yields elsewhere is vital for making informed decisions.
Long-Term Implications of Rising Yields
The highest Japan 40-year government bond yield in 16 years holds long-term implications for both the yield curve and monetary policy in Japan. As yields rise, they can affect borrowing costs, consumer spending, and even corporate investments. This environment can help to shape fiscal strategies and economic growth plans moving forward.
Central banks may find themselves needing to adjust their monetary policy approaches to respond to these changing conditions, impacting overall economic stability. As trends evolve, market participants—especially bond investors—must stay informed and adaptable.
Conclusion
In summary, the current performance of the Japan 40-year government bond yield is reflective of broader global yield trends and U.S. Federal Reserve rate cuts. As we navigate these changing dynamics, it becomes increasingly important for bond investors to grasp how international monetary policies can impact their investments. The bond market continues to evolve, and understanding these shifts will be crucial for future investment strategies.
With careful attention to global yields and the U.S. Federal Reserve’s decisions, investors can better position themselves for success in the ever-changing financial market landscape.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the Japan 40-year government bond yield?
The Japan 40-year government bond yield is the interest rate the Japanese government pays to borrow money for 40 years. It serves as a critical indicator of financial market conditions and can signal broader economic trends.
Why have yields on Japanese government bonds fluctuated?
Yields have fluctuated significantly in the past 16 years due to various economic factors, including inflation expectations, central bank interest rates, and global market dynamics. Recently, a surge in yields marks a departure from the historically low rates seen earlier.
How do global yields affect Japan’s bond yield?
Global yields influence Japan’s bond yield through interconnected financial markets. Changes in interest rates in major economies, like the U.S., can impact investment flows and overall market sentiment, directly affecting Japan’s bond yields.
What role does the US Federal Reserve play in the Japanese bond market?
The US Federal Reserve’s monetary policy decisions, particularly regarding interest rate cuts, can lead to increased investments in foreign bonds, including Japanese bonds. This can directly impact the Japan 40-year government bond yield.
What are the current bond market trends affecting Japan’s bond yield?
Current trends show that as interest rates rise globally, government bond yields in countries, including Japan, tend to climb as well. This can be a gradual process or a rapid change depending on market conditions and investor sentiment.
What are the long-term implications of rising yields on the Japan 40-year government bond?
Rising yields can impact borrowing costs, consumer spending, and corporate investments in Japan. It may also prompt central banks to adjust their monetary policy to maintain economic stability, affecting broader fiscal strategies and growth plans.
How should bond investors respond to these changes?
Bond investors should stay informed about global economic shifts and how they affect local yield trends. Understanding these dynamics can help investors make timely and informed decisions about their portfolios.





