This study evaluated data from 44,502 unique patients, with a median follow-up of 1,874 days. The majority of patients were older men with initial cancer diagnosis and independent in daily activities. A total of 175,624 diagnosis records and over 15 million prescription orders were analyzed. The results highlighted significant hazards for adverse events linked to various anticancer therapies, with specific drug comparisons showing notable differences in risks for conditions like peripheral neuropathy and oral mucositis. Sensitivity analyses demonstrated attention to potential errors in data extraction, further emphasizing the study’s findings on the safety profiles of different cancer treatments.
Title: Key Findings on Patient Data and Adverse Events in Anticancer Treatments
In a recent study, researchers analyzed a substantial amount of patient data, evaluating a total of 44,502 unique patients, with 59.6% being male and 40.4% female. The comprehensive data collection included nearly 176,000 diagnosis procedures and over 3.9 million prescriptions. Each patient generated an average of approximately 3.9 diagnosis reports and an impressive 253 prescription orders. The study was extensive, with patient follow-ups averaging 1,874 days.
The characteristics of the patients revealed that a significant majority, about 59.5%, were aged 65 years or older. Most patients had an initial cancer diagnosis, with digestive organs being the most common site, accounting for 40.8% of cases. The analysis also noted that high percentages of patients were independent in their daily activities, indicating a relatively good quality of life even amid their health battles.
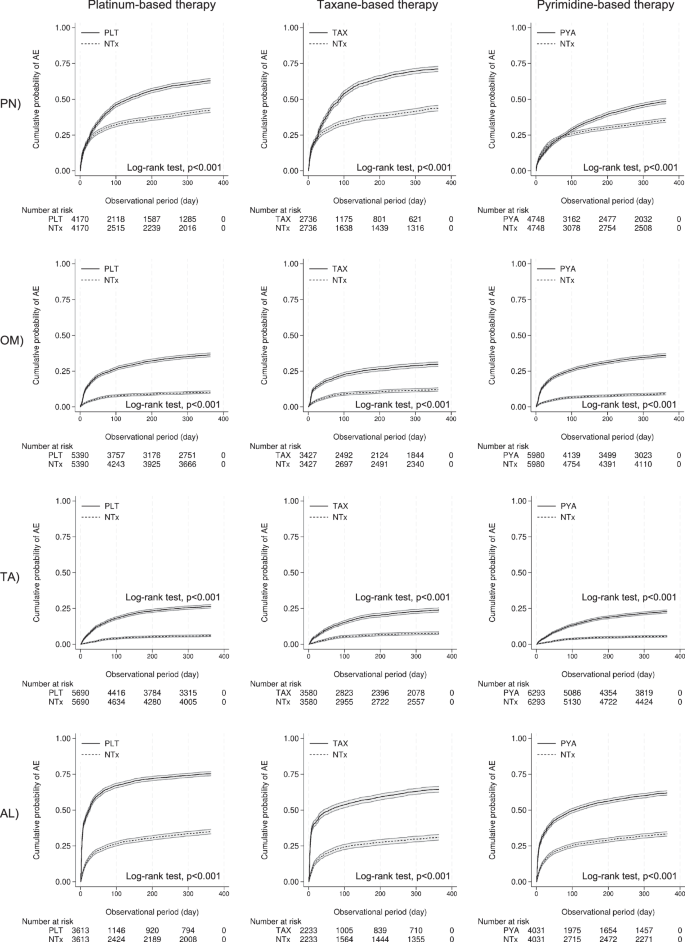
Moreover, the research delved into adverse events associated with different types of anticancer therapies. Notably, significant differences were found in the occurrence of peripheral neuropathy and oral mucositis among various treatment groups. For example, the hazard ratio (HR) for adverse events with platinum-based therapies was considerably high, particularly for oral mucositis, which highlights the importance of careful monitoring during treatment.
The study also explored the role of natural language processing in evaluating patient outcomes, shedding light on potential discrepancies in data extraction and analysis. Sensitivity analyses showed that while many cases remained unaffected by these errors, some variations influenced the overall outcomes.
These findings are essential as they provide critical insights into patient care, treatment effectiveness, and the potential side effects of anticancer therapies, emphasizing the need for tailored patient management plans.
Tags: Patient data, Anticancer treatments, Adverse events, Cancer study, Treatment effectiveness, Peripheral neuropathy, Oral mucositis, Healthcare analysis.
What is post-Marketing surveillance for anticancer drugs?
Post-Marketing surveillance is a way to monitor the safety and effectiveness of cancer drugs after they are approved and used by patients. It helps find out how these drugs work in real-life situations.
How does natural language processing help in this surveillance?
Natural language processing, or NLP, is a technology that can read and understand written text. It helps researchers analyze electronic medical records to find important safety information about cancer drugs.
What types of information can be gathered from electronic medical records?
Researchers can gather data on side effects, how well the drug works, patient reactions, and overall health outcomes from electronic medical records. This information is crucial for understanding the drug’s impact on patients.
Why is it important to monitor anticancer drugs after they are approved?
It’s important because some side effects or issues may only show up when many people use the drug over time. Monitoring helps ensure patient safety and improves future treatment options.
Who benefits from post-Marketing surveillance of anticancer drugs?
Patients, doctors, and researchers all benefit. Patients get safer treatments, doctors can make better decisions, and researchers gain valuable insights to develop new drugs and improve existing ones.