Artificial intelligence (AI) agents act as helpful assistants in businesses, working quietly to improve productivity and resolve issues. These agents can autonomously carry out tasks, allowing employees to focus on more complex work. AI agents follow a process: they receive instructions, plan their next steps, gather necessary data, and complete tasks based on set conditions. While they currently need human input to function effectively, future developments like agentic AI aim to enhance their capabilities. Industries can benefit from AI agents with increased efficiency, cost savings, better decision-making, and improved customer satisfaction. With proper governance and support, AI agents can transform ordinary business operations into streamlined processes, adapting to various needs.
The Future of AI Agents: Boosting Productivity and Efficiency

Our modern lives are increasingly enhanced by artificial intelligence (AI) agents. These helpful assistants work silently in the background, tackling issues, streamlining processes, and ultimately driving business productivity.
AI agents, also known as enterprise agents, are designed to perform tasks autonomously. With these agents at work, human employees can focus on higher-value responsibilities while organizations achieve greater efficiency. Each AI agent comprises three main components:
- Architecture: This refers to where the AI is hosted—be it in the cloud, a hybrid model, or on-premises.
- Function: The processes they employ to collect and analyze data.
- Program: The development, training, and deployment methodology for the agents.
Understanding How AI Agents Operate
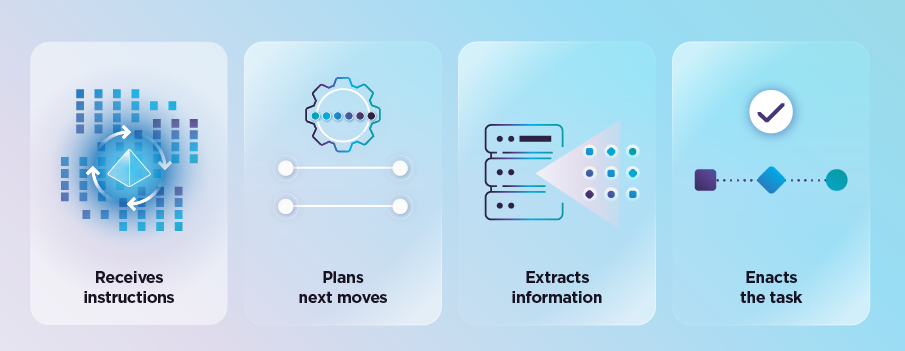
Today’s AI agents, while powerful, are not completely autonomous. They currently function with a human-in-the-loop, setting the rules and providing the necessary knowledge base to tackle various tasks. The workflow usually involves:
- Receiving instructions: AI agents are programmed to achieve specific goals.
- Planning moves: They break down these goals into manageable tasks.
- Extracting information: Agents gather the necessary data, interacting where applicable.
- Executing tasks: They perform the tasks to reach the set objectives.
The Different Types of AI Agents
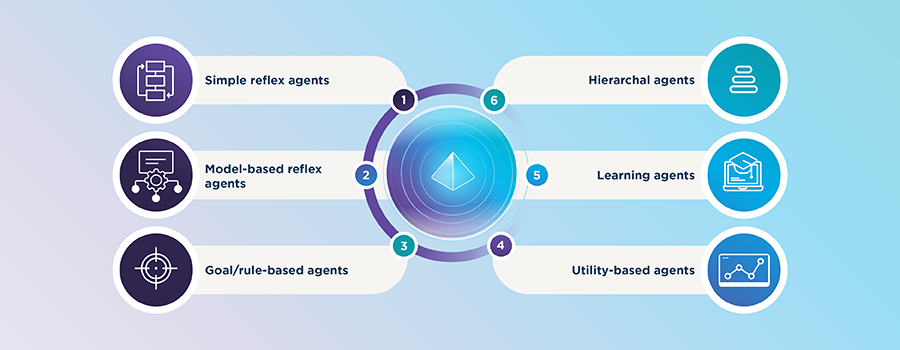
There are various kinds of AI agents. Here are some common types:
Simple Reflex Agents
These agents respond to specific conditions with predefined actions. An example is a thermostat that activates heating at a designated time.
Model-Based Agents
More sophisticated than reflex agents, these agents keep an internal state that helps them deal with partly observable environments, like a robot vacuum navigating a room.
Goal-Based Agents
These agents plan their actions towards achieving specific goals, like an autonomous car that navigates safely from one location to another.
Utility-Based Agents
Utility-based agents evaluate multiple options and choose the one that maximizes benefits, akin to a GPS that finds the best driving route considering various factors.
Learning Agents
These agents learn from experience, improving performance over time, similar to a spam filter that gets better at identifying junk mail by analyzing past data.
Hierarchical Agents
This type oversees other agents, managing complex operations efficiently within organizations.
Preparing for AI Agent Implementation
As organizations look to deploy AI agents, they must ensure quality and governance. Essential considerations include:
- Data Privacy: Be aware of data security requirements.
- Ethics: Monitor for biases and inaccuracies.
- Technical Skills: Developers need expertise in the AI systems being implemented.
- Computational Needs: Be prepared for the costs and environmental impacts of AI resources.
The Upcoming Impact of Agentic AI
The development of agentic AI, which involves conversational tools that learn from interactions, promises significant benefits:
- Increased Productivity: AI agents can handle repetitive tasks, freeing humans for creative work.
- Cost Savings: Reducing errors and inefficiencies lowers operational costs.
- Better Decisions: Enhanced access to data helps in informed decision-making.
- Improved Customer Satisfaction: Personalized experiences arise from intelligent data usage.
AI agents are set to revolutionize work dynamics. By leveraging generative AI, organizations can enhance their capabilities even further. The key to success lies in selecting a suitable AI agent system that aligns with your business goals.
What are AI Agents? The Future of Automation
FAQ 1: What is an AI agent?
An AI agent is a computer program that can perform tasks automatically, using smart technology. It learns from data and makes decisions without needing much human help.
FAQ 2: How do AI agents work?
AI agents work by collecting and analyzing data. They use algorithms to understand patterns and make predictions. This helps them complete tasks faster and smarter.
FAQ 3: What are some examples of AI agents?
Some common examples include virtual assistants like Siri and Alexa, chatbots for customer service, and recommendation systems on streaming platforms. These AI agents help people interact with technology easily.
FAQ 4: Why are AI agents important for automation?
AI agents are key for automation because they can handle repetitive tasks efficiently. This saves time and reduces the chance of errors. Businesses can focus on more complex work while AI agents manage simple jobs.
FAQ 5: What does the future hold for AI agents?
The future of AI agents looks bright. They will become more advanced, understanding human emotions and needs better. This will lead to improved customer service, smarter homes, and even better healthcare solutions.






