Swiss inflation has entered a phase of unexpected slowdown, prompting crucial discussions about its implications for monetary policy and economic stability. Understanding the current inflation rate trends in Switzerland is essential, as they influence the central bank’s target and potential interest-rate cuts, shaping the broader economic outlook.

Understanding Swiss Inflation
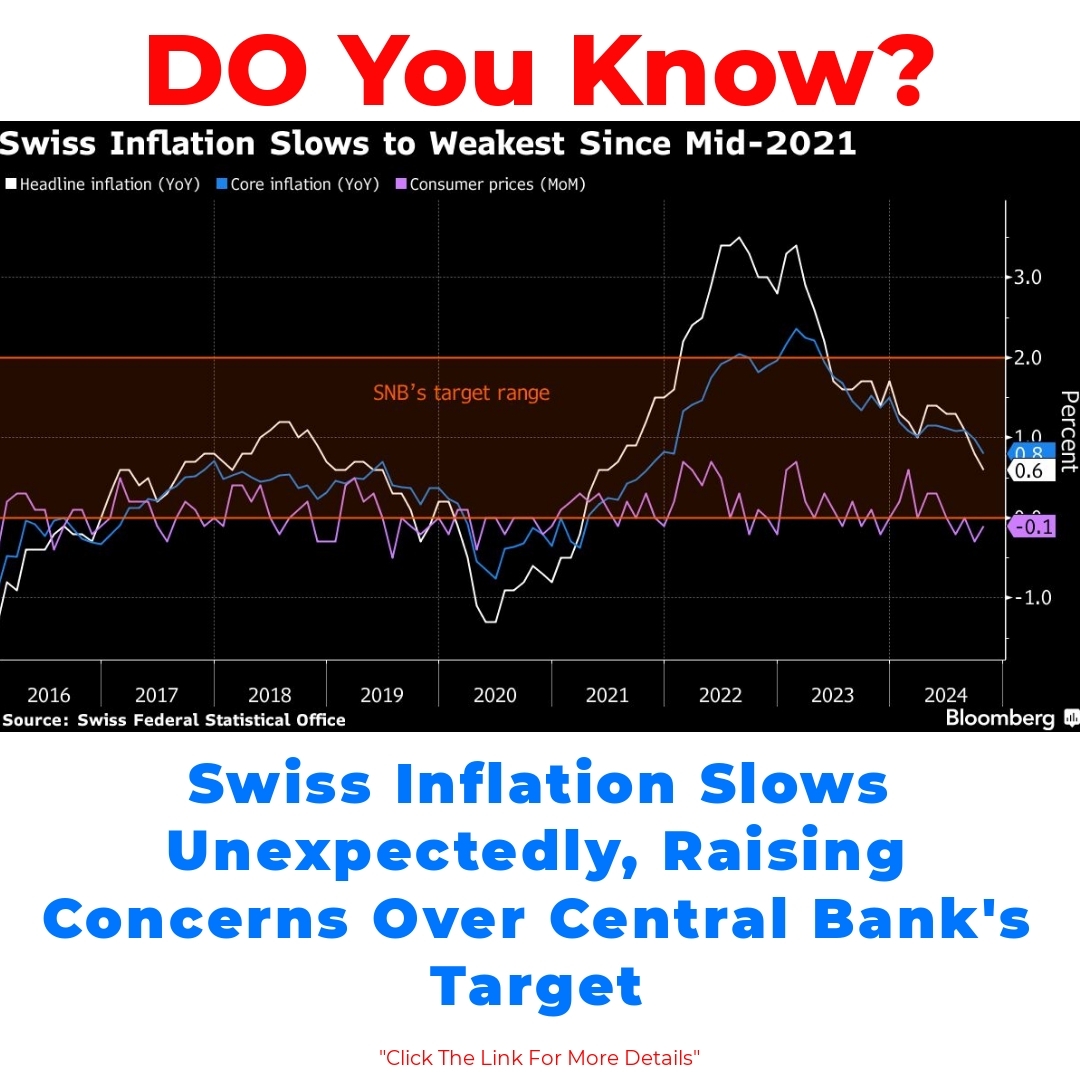
Current Swiss Inflation Rate Trends 2023
The current state of Swiss inflation has shown some fascinating trends in 2023. Recent statistics indicate that the inflation rate has unexpectedly slowed down, prompting both consumers and policymakers to take notice. Compared to previous years, where inflation was on the rise, this year’s figures suggest a shift in the economic landscape.
– For instance, in the past few years, inflation rates were hovering around higher percentages, making it a significant concern for many.
– Now, with the latest data, we’re seeing a percentage drop that might change how the Swiss National Bank (SNB) approaches its monetary policy.
Factors contributing to the current inflation rate are varied, including global supply chain issues, changes in consumer demand, and economic responses to the ongoing effects of the pandemic.
The Central Bank Target for Inflation
The Swiss National Bank has a clear target when it comes to inflation— specifically, it aims to keep it within a specific range. Understanding this central bank target is crucial because it guides the bank’s decisions on interest rates and other monetary policies.
Currently, the lower inflation figures are providing a context that is quite different from what we experienced just a year ago. This may lead to more room for adjustments in how the SNB manages its economic strategies, particularly regarding interest rates.
The Role of Interest-Rate Cuts
Potential for Further Interest-Rate Cuts
When inflation slows down, as we’re observing with Swiss inflation, there’s potential for further interest-rate cuts. Recent monetary policy decisions made by the SNB reveal a cautious but open approach to these adjustments.
The case for interest-rate cuts grows stronger as slower inflation could lead to stabilized economic conditions. Such measures could also encourage spending and investment, which are vital for economic growth.
Impact of Interest-Rate Cuts on the Swiss Economy
Historically, interest-rate cuts in Switzerland have had significant impacts. Lower interest rates mean cheaper borrowing costs, which can spur both consumer spending and business investments.
Some anticipated effects include:
– Enhanced economic stability for various sectors.
– Potential increases in production as businesses look to expand.
– What’s more, consumers might feel a bit more financially secure, leading to higher expenditure.
These outcomes showcase the delicate balance the SNB must maintain in steering the economy through changing inflation dynamics.
Economic Outlook Amid Slow Inflation
Predictions for Future Inflation Rates
Looking ahead, economists are trying to predict what the future holds for inflation rates in Switzerland. Various economic forecasts provide insights that can shape expectations around not only Swiss inflation but also the central bank’s future interest rate decisions.
Several factors could influence future inflation trends, including changes in global markets, shifts in consumer behavior, and potential geopolitical tensions. Staying informed on these aspects can offer a clearer picture of the economic outlook.
How Inflation Affects Central Bank Decisions in Switzerland
There exists a critical relationship between inflation, monetary policy, and the actions of the central bank in Switzerland. As inflation rates fluctuate, decisions regarding interest-rate cuts or hikes become increasingly complex.
If the SNB finds itself undershooting its central bank target, it may have to adjust its strategies. This could mean introducing new measures to stimulate the economy and align inflation closer to its target.
Comparisons with Global Trends
Interest-Rate Cuts in Other Countries
Taking a global perspective, many countries have also been implementing interest-rate cuts in response to similar inflation dynamics. Observing these trends helps to contextualize how Switzerland’s monetary policy stacks up against others.
For example:
– Countries like the United States and the European Union have been adjusting their rates to combat inflation.
– Comparing Switzerland’s decisions with these nations reveals differing approaches influenced by local economic conditions and political climates.
Economic Stability on a Global Scale
Indeed, the interconnectedness of global economic trends plays a huge role in shaping Switzerland’s economic environment. Change in international inflation rates could directly impact Swiss monetary policy, as the economy is not isolated from global influences.
Factors like international trade dynamics, currency fluctuations, and global supply chains can all sway local inflation and economic stability, making it essential for policymakers to remain vigilant.
Conclusion
In wrapping up, the current state of Swiss inflation invites significant consideration, particularly regarding potential interest-rate cuts. As the country navigates this unexpected slowdown, it becomes increasingly important to maintain economic stability while striving to meet the central bank’s targets.
Moving forward, keeping an eye on how inflation dynamics evolve will be key in shaping both monetary policy and the overall economic outlook for Switzerland. By understanding these trends, individuals and businesses can better prepare for what lies ahead in the Swiss economy.
FAQ about Swiss Inflation
What is the current inflation rate in Switzerland for 2023?
The current inflation rate in Switzerland has shown a slowdown compared to previous years, with recent statistics indicating a notable drop in inflation percentages.
What factors are influencing the current inflation rate?
Several factors contribute to the current inflation rate, including:
- Global supply chain issues
- Changes in consumer demand
- Economic responses to the ongoing effects of the pandemic
What is the Swiss National Bank’s target for inflation?
The Swiss National Bank aims to maintain inflation within a specific range. Understanding this target is essential as it guides the bank’s decisions on interest rates and other monetary policies.
Will there be further interest-rate cuts in Switzerland?
Yes, the potential for further interest-rate cuts exists as the inflation rate slows. This could stabilize economic conditions and encourage spending and investment.
How do interest-rate cuts impact the Swiss economy?
Interest-rate cuts generally lead to:
- Cheaper borrowing costs for consumers and businesses
- Increased consumer spending
- Potential economic stability across various sectors
- Higher production as businesses expand
What are the predictions for future inflation rates in Switzerland?
Economists predict that future inflation rates may be influenced by:
- Changes in global markets
- Shifts in consumer behavior
- Potential geopolitical tensions
How does inflation affect the Swiss National Bank’s decisions?
Inflation rates directly influence the Swiss National Bank’s monetary policy. If inflation remains below its target, the bank may adjust its strategies to stimulate the economy.
How does Switzerland’s inflation and monetary policy compare to other countries?
Many countries, including the United States and the European Union, are adjusting their interest rates in response to inflation dynamics, which can provide context for Switzerland’s own policies.
What role does global economic stability play in Swiss inflation?
The interconnectedness of global economic trends significantly shapes Switzerland’s economic environment, where international factors like trade dynamics and currency fluctuations can impact local inflation.






