The China local debt market is experiencing unprecedented challenges, marked by record high defaults that have sent shockwaves through the financial landscape. Local government debt plays a crucial role in funding essential projects, but rising defaults threaten investor confidence. This article delves into the intricacies of China’s local debt situation and its far-reaching implications.

The Dynamics of China’s Local Debt Market
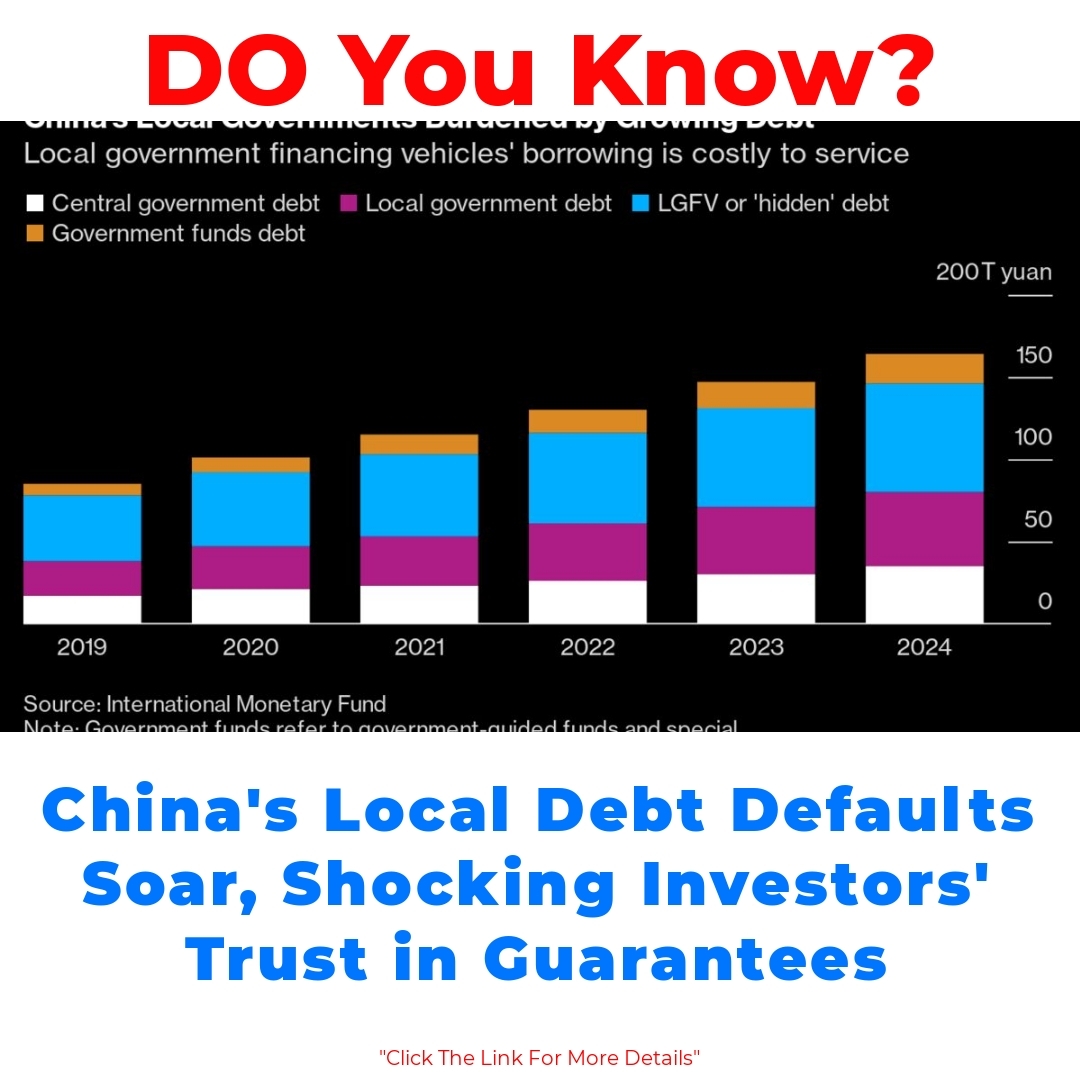
Understanding the China local debt market starts with knowing what local government debt really is. Essentially, local governments in China need money to finance various projects—from infrastructure to public services. They often turn to the municipal bonds market, which allows them to raise funds efficiently. But how does this all come together?
Local governments create regional financing vehicles. These are entities set up to issue bonds, enabling local authorities to access funds for their projects. This system has become crucial for local governments as they seek to develop their regions. However, it’s a double-edged sword, as it contains risks that many investors may not fully appreciate.
Recent Trends in Debt Defaults in China
Over recent years, the statistics surrounding debt defaults in China have become alarming. The surge in record high defaults in the local debt market is impossible to ignore. Just to put it in perspective, analysts have noted a sharp increase in the number of local governments failing to meet their debt obligations. But why is this happening?
Several factors play a role in this trend. Firstly, the rapid pace of urbanization has led to excessive borrowing. Local governments, eager to fund numerous projects, borrowed heavily, often without a clear revenue stream to support repayment. Moreover, an economic slowdown hasn’t helped, making it harder for these governments to generate the income needed to service their debts.
Misconceptions About State Implicit Guarantees
A critical concept that many investors cling to when engaging with local government debt is the idea of a state implicit guarantee. In theory, this implies that the central government will step in to bail out local governments in distress. However, this assumption might be flawed.
Many investors assume that their investments in local government debt are safe due to this guarantee. The reality, however, is quite different. With the recent rise in defaults, the belief in such guarantees is crumbling. The collapse of this misconception could have severe implications for future investments and overall market confidence.
Implications of Local Debt Defaults
The implications of these local debt defaults extend beyond the immediate investors in China. A rising tide of defaults could contribute to a broader economic malaise, potentially signaling a China financial crisis. When local governments default, it could ripple through the economy, affecting everything from local services to employment rates.
Additionally, if defaults increase, this could alter the landscape of sovereign debt in China. Investors might become more cautious, leading to increased borrowing costs and further tightening credit markets. Market confidence could diminish, prompting investors to reconsider their strategies when engaging with local government debt.
Risk Assessment for Investors
For investors, understanding local debt risks has never been more critical. Individual and institutional investors alike need to carefully evaluate the potential pitfalls. Conducting thorough due diligence is essential, involving a deep dive into regional economic conditions and fiscal responsibility of local governments.
Here are a few tips for navigating the current turmoil in the local debt market:
– Stay informed about local government financial health.
– Diversify investments to mitigate risks associated with defaults.
– Monitor broader economic indicators that may impact local debt sustainability.
Conclusion
In summary, the situation surrounding China’s local government debt is complex, filled with challenges and opportunities. The record high defaults in China’s local debt market signify a pivotal moment for investors. Preparing for these future trends is essential for anyone looking to engage with this sector.
Investors must enhance their understanding of their investments and remain vigilant about the evolving landscape of local debt. As we move forward, the lessons learned from this challenging environment will be invaluable for navigating China’s financial future. Whether you’re keeping tabs on local government debt or gauging how it impacts your portfolio, having a clear picture of this market is key to making informed decisions.
FAQ
What is local government debt in China?
Local government debt in China refers to the money that local authorities borrow to finance projects like infrastructure and public services. They often do this by issuing municipal bonds through regional financing vehicles.
Why are there recent trends in debt defaults?
Recent trends in debt defaults are largely due to excessive borrowing by local governments without proper revenue streams to repay. Rapid urbanization and an economic slowdown have further exacerbated these issues.
Are state implicit guarantees for local government debt reliable?
Many investors believe that the central government will bail out local governments in distress. However, this assumption is proving to be flawed as defaults rise, leading to decreased confidence in these guarantees.
What are the implications of local debt defaults?
Defaults can lead to economic repercussions, affecting local services and employment rates. They may also result in increased borrowing costs and tighter credit markets, causing investors to rethink their strategies.
How can investors assess risks in the local debt market?
Investors should:
- Stay informed about the financial health of local governments.
- Diversify investments to reduce risk from defaults.
- Monitor broader economic indicators that affect local debt sustainability.






